WHAT IS STAGFLATION? WHY DO WE HAVE IT?
- admin

- Sep 1, 2022
- 3 min read

WHAT’S STAGFLATION?
Stagflation is an economic environment when the economy is stagnant and prices rise fast.
The last time we had stagflation was the 1970 decade. At that time, CPI growth rates were high at 5.8% in 1970 and 13.55% in 1980.

(U.S. CPI Growth and Unemployment Rates 1945-2022, FED)
In that period, the US economy was struggling with high unemployment rates (5% to 10%).
Why do people pay attention to the stagflation phenomenon?
Reason is that most economists believe that CPI growth rate and unemployment rate move in the opposite directions, which is when one falls, the other rises. When the CPI growth rate is high, it means the economy is hot and doing well. Therefore, the unemployment rate is low. On the other hand, when the CPI growth rate is low, the economy is struggling and the unemployment rate is high. People find it difficult to explain the stagflation phenomenon because it doesn’t fit into the popular beliefs.
WHY DOES STAGFLATION HAPPEN?
From the above chart, we can see that CPI growth rate and unemployment rate are moving together but there’s a time lag between the two.
Also, CPI growth rate is a leading indicator while unemployment rate is a lagging indicator.
In the stagflation period (1970s), the time lag was about 1-2 years.
In the normal period (1980-2020), the time lag was 2-5 years, which is longer than the stagflation period.
2 questions:
Why do CPI growth and unemployment rates move together? Why is there a time lag between the two?

At the start of a business cycle, CPI is low. CPI growth rate rises due to money printing and credit expansion. This causes economic booms and unemployment rate falls. The impact of expansion of money and credit in economic growth diminishes over time. Businesses start to fail and unemployment starts to rise. That’s when the bottom of the unemployment rate has been reached. According to the prominent economist Mises of Austrian Economic School, the reason businesses fail eventually when credit and money keep expanding is because when credit and money supply expand, interest rate falls. Falling interest rates cause capital consumption which leads to lower economic output later on.
This shows CPI growth and unemployment rates move together but there’s a lag.
The lag is longer when CPI growth rate is low (normal period) and the lag is shorter when CPI growth rate is high (stagflationary period)
Why was the time lag is shorter when CPI growth rate was high in the 1970s?
CPI growth rate reflects the growth of the money and credit supply. When expansion is too fast, real income falls quickly because wage gains can’t catch up with price increases. People are poorer with falling real income and they cut back consumption. At the same time, quickly rising prices of raw materials eat into business profit margins and make businesses less profitable. This leads to more lay-off and rising unemployment.
In short, quick money printing and credit expansion (high CPI growth rate) kills off the economy and leads to high unemployment.
ARE WE IN A STAGFLATION ENVIRONMENT? WHY?
Yes, we are currently in a stagflation environment.
The official CPI growth rate is above 8%. Unofficial CPI rates are 15-20%. How do we know? Look at changes in your grocery prices in the last 1 year. Another source is shadowstats. The US gov has manipulated the CPI and suppressed it since the 1980s.
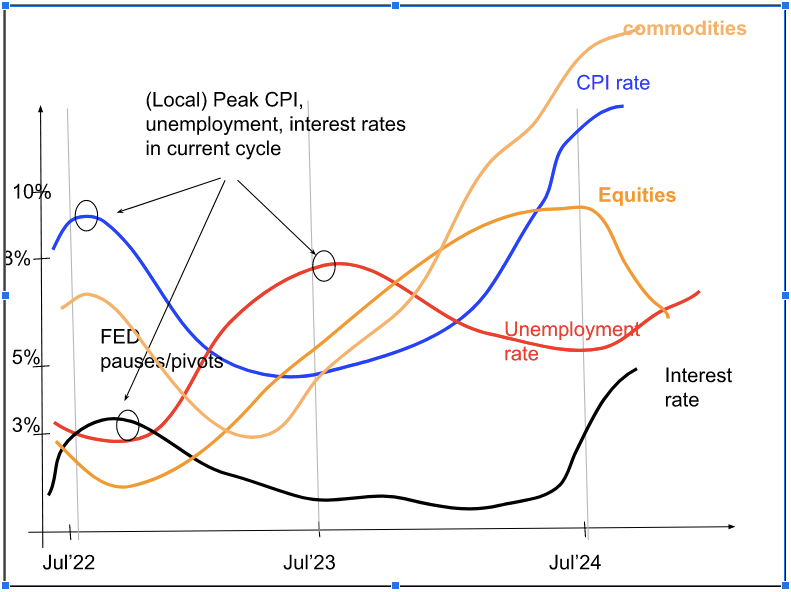
Based on the above explanation, I’d expect the unemployment rate to increase next year. Since the FED is raising rates aggressively, expect the interest rate to peak by the end of this year. Therefore, CPI growth rate peaked at 9% last month in July 2022 in this cycle. We are currently in a recession and unemployment will start to rise and peak in the 2nd half of 2023.
This is my projection where interest rates, CPI, unemployment and financial assets will be in the next 2 years.
CPI peaks Jul 2022
Unemployment will start rising
FED will pause and start cutting interest rates end 2022/early 2023
Equities, bonds, commodities are still falling now and will find bottoms in Oct/Nov when FED signals pause/pivot. They will rally until CPI rises again.



Comments